
Description
In the world of electrical engineering and circuit protection, fuse holders play a crucial yet often underappreciated role. These essential components serve as the housing for fuses, allowing for safe installation, secure contact, and efficient replacement when necessary.
Whether in residential wiring systems, industrial machinery, or automotive applications, the importance of choosing the correct fuse holder cannot be overstated.

This article provides a comprehensive overview of fuse holders, including their types, primary functions, and common applications—helping engineers, technicians, and procurement professionals make informed decisions.
A fuse holder is a device specifically designed to securely mount a fuse and provide reliable electrical contact between the fuse and the circuit. It simplifies the process of fuse replacement and contributes to the overall safety of the system by preventing accidental contact with live electrical parts.
Typically made from durable, non-conductive materials such as thermoplastics or phenolic resins, fuse holders are engineered to handle different voltages, currents, and environmental conditions.
The fuse itself is a sacrificial component, designed to "blow" and interrupt current when excessive current flow threatens the circuit. However, without a proper holder, the fuse may not be installed correctly, may not function reliably, or could even become a safety hazard.
Here’s why fuse holders are vital:
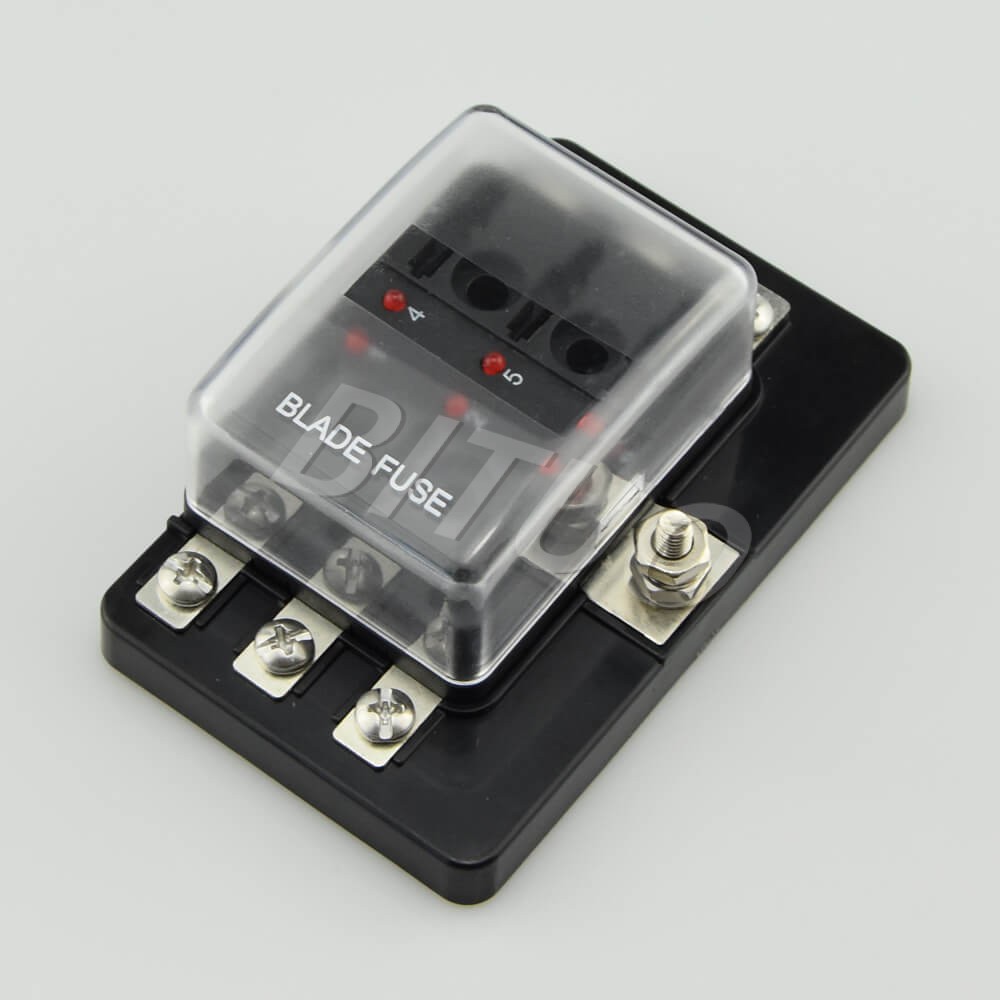

Fuse holders are classified based on their design, installation method, and the type of fuse they support. Below are the most common types:

When selecting the appropriate fuse holder, several technical factors must be evaluated:
Fuse holders are found in virtually every industry where electrical systems are used. Here are some key examples:
Control panels, programmable logic controllers (PLCs), and motor starters use panel mount and DIN rail fuse holders to protect sensitive electronics.
Inline fuse holders are frequently used in automotive wiring harnesses, protecting circuits for lighting, infotainment systems, and more.
Circuit protection in lighting systems, HVAC units, and kitchen appliances relies on fuse holders to ensure safety and compliance.
Solar inverters and battery storage systems often use high-current fuse holders, especially those with weatherproof enclosures.
PCB-mounted fuse holders are integrated into devices like televisions, routers, and audio equipment for compact, efficient protection.
To ensure performance and safety, fuse holders must adhere to international standards such as:
IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission)
RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances)
These standards define material properties, mechanical strength, insulation resistance, and fire safety requirements.
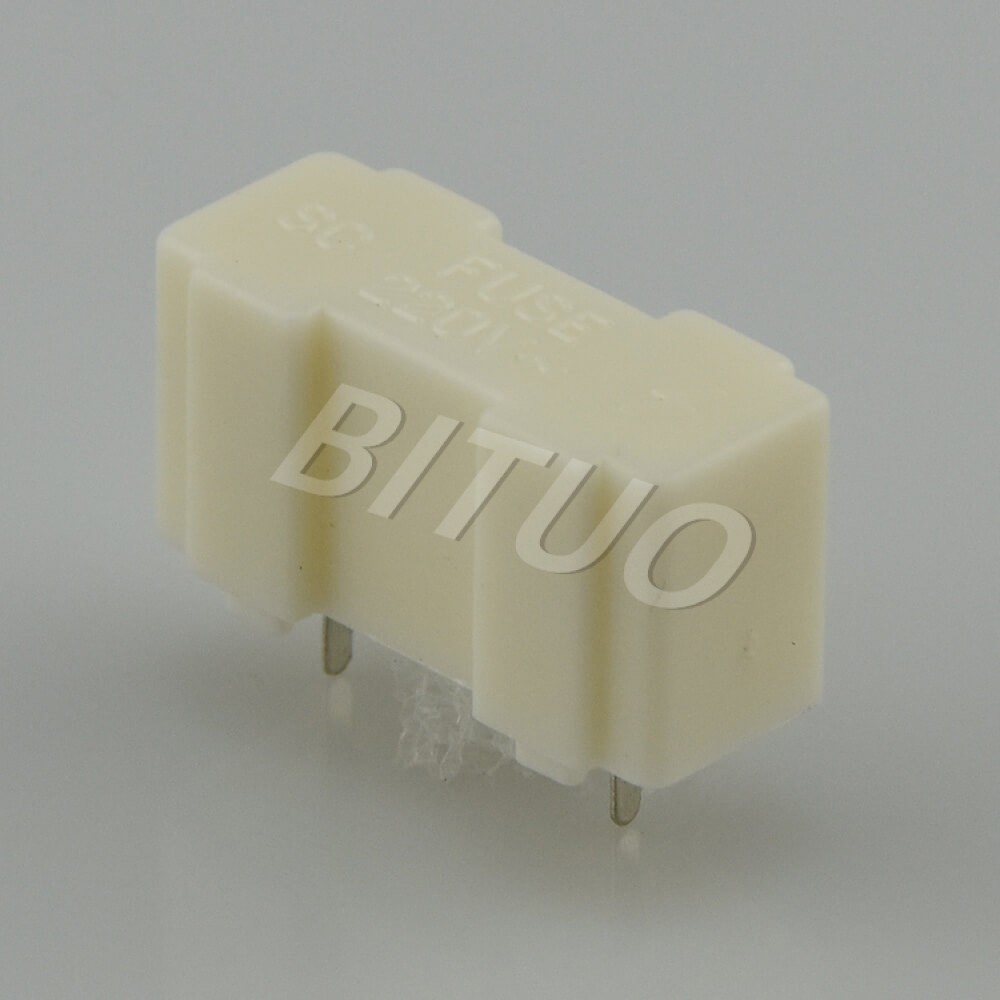
While small in size, fuse holders perform a mighty function in safeguarding electrical systems across every sector. Understanding the differences among various types—and their proper applications—ensures not only circuit protection but also system longevity and user safety. As electronic systems continue to evolve, so does the importance of reliable, high-performance fuse holders.
Whether you're designing a new product, maintaining an existing system, or sourcing components for a large-scale application, choosing the right fuse holder is an investment in reliability and safety.
Reviews
To write a review, you must login first.
Similar Items